2. Functionalist Perspective
According to functionalism society is a system of interconnected parts that work together in harmony to maintain a state of balance and social equilibrium.
For example, each of the social institutions contributes important functions for society:
- Family provides a context for reproducing, nurturing, and socializing children
- education offers a way to transmit a society’s skills, knowledge, and culture to its youth
- politics provides a means of governing members of society
- economics provides for the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services
- religion provides moral guidance and an outlet for worship of a higher power.
- For example, the increase in single- parent and dual-earner families has contributed to the number of children who are failing in school because parents have become less available to supervise their children’s homework.
- As a result of changes in technology, colleges are offering more technical programs, and many adults are returning to school to learn new skills that are required in the workplace.
- The increasing number of women in the workforce has contributed to the formulation of policies against sexual harassment and job discrimination.
- Elements of society are functional if they contribute to social stability and dysfunctional if they disrupt social stability.
- Some aspects of society can be both functional and dysfunctional.
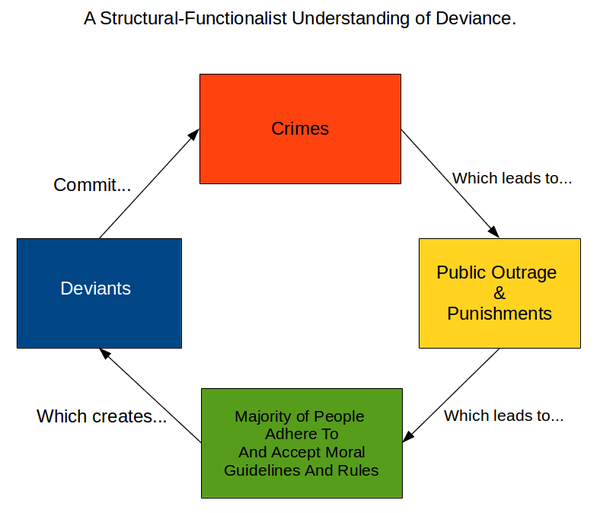
- For example, crime is dysfunctional in that it is associated with physical violence, loss of property, and fear. But crime is also functional for society because it leads to heightened awareness of shared moral bonds and increased social cohesion.
- Manifest functions are consequences that are intended and commonly recognized.
- Latent functions are consequences that are unintended and often hidden.
- For example, the manifest function of education is to transmit knowledge and skills to society’s youth. But public elementary schools also serve as babysitters for employed parents, and colleges offer a place for young adults to meet potential mates. The baby-sitting and mate-selection functions are not the intended or commonly recognized functions of education; hence they are latent functions.
Answer the following questions after watching the first ten minutes of the video above.
A. What is deviance?
B. What are some examples of deviance?
C. What are some examples of informal social control?
D. What are some examples of formal social controls?
E. How does the functionalist theory explain crime and deviance?
Be sure to explain how crime:
- identifies the failure of social structures
- reinforces the societal norms and promote social unity
- lead to social change